The energy of the sun is harvested by green plants and is converted into chemical energy or food molecules. This food energy is passed on to the heterotrophic organisms or consumers of the ecosystem in a series of steps. So, let’s find out what are the trophic levels in a food chain.
What are the Trophic Levels in a Food Chain?
The word trophic comes from the Greek word “trophe” which means food. The entire series of organisms through which food energy moves in an ecosystem, by eating and being eaten is called a food chain and each step in the food chain is called a trophic level.
Depending on various criteria, these trophic levels become part of different types of ecological pyramids. Each trophic level in the pyramid consists of organisms that have similar food habits or consume the same type of organisms. Thus the producers and consumers of an ecosystem can be arranged into several feeding groups or trophic levels.
- The first level is occupied by the producers
- Herbivores represent the second trophic level
- Primary carnivores represent the third trophic level
- Top carnivores represent the last level
- The last trophic level belongs to decomposers
Food Chains
Green plants synthesize food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. Solar energy is thus stored as chemical energy in organic compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc.
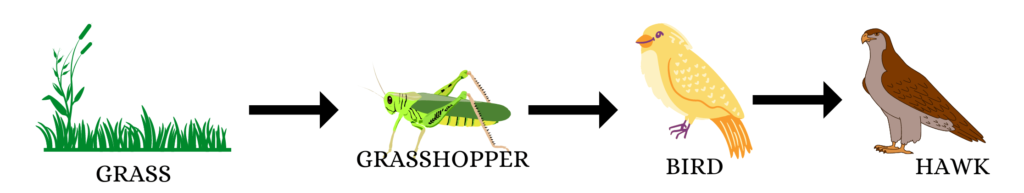
The food manufactured by green plants is used by themselves and by herbivores. Herbivores are eaten by carnivores. This way, one form of life supports the other form. Thus food from one trophic level reaches the other trophic level and a food chain is established. This is called the food chain. For eg.,
- Marsh grass is consumed by grasshoppers.
- Grasshopper is eaten by a bird.
- The bird is consumed by a hawk.
The resultant food chain can be written as,
Marsh Grass —> Grasshopper —> Bird —> Hawk.
Food chains are of different types.
- The predator type starts from plants and goes from smaller to larger animals. This is known as the grazing food chain.
- The parasitic chain goes from larger to smaller organisms (Tree – birds – lice). This is an example of a parasitic food chain.
- The saprophytic chain goes from dead matter to microbes to earthworms to frogs to snakes to birds. This type of food chain is called the detritus food chain.
Food Web
Several food chains in an ecosystem connect the carnivores to the producers. More than one interconnected food chain that forms a network pattern is called a food web.
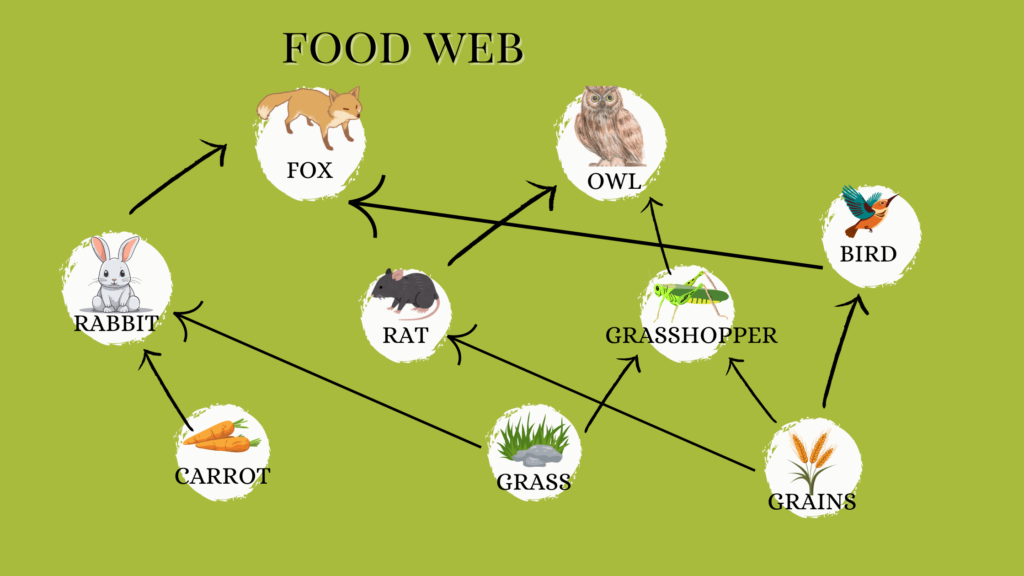
Each trophic level has a great diversity of organisms. It may also happen that an organism at any trophic level may draw its food from two or more different organisms of a lower trophic level. Marsh plants are eaten by a variety of insects, birds, animals, and fishes.
Some animals are prey for several predators. Sometimes, mice are directly eaten by owls and not just by snakes. This type of interrelationship interlinks all the individuals of the whole community. In this way, the food chain makes up a food web.
Conclusion
Trophic levels and food chains help understand the various interrelationships happening in an ecosystem. Processes such as decomposition, and relationships such as predation, herbivory, mutualism, commensalism, etc are used to understand the stability of an ecosystem. Trophic levels and food chains are the key to all these interrelationships between organisms.
References
Trophic level – Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary. (2023, September 1). Biology Articles, Tutorials & Dictionary Online. https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/trophic-level




