The different types of life cycle in algae or alternation of generations are based on the various morphological and cytological changes happening inside the plant body.
Each of these changes will be happening systematically and will be similar in plants of the same group or division. There are 5 main types of life cycles in algae.
- Haplontic
- Diplontic
- Diplohaplontic
- Haplobionic
- Diplobiontic
Haplontic type of life cycle in algae
The haplontic life cycle in algae is also called monogenetic. This is one of the most common types of life cycle in algae with two phases. The haploid gametophytic phase is the prominent one here with the diploid phase seen only in the zygote.
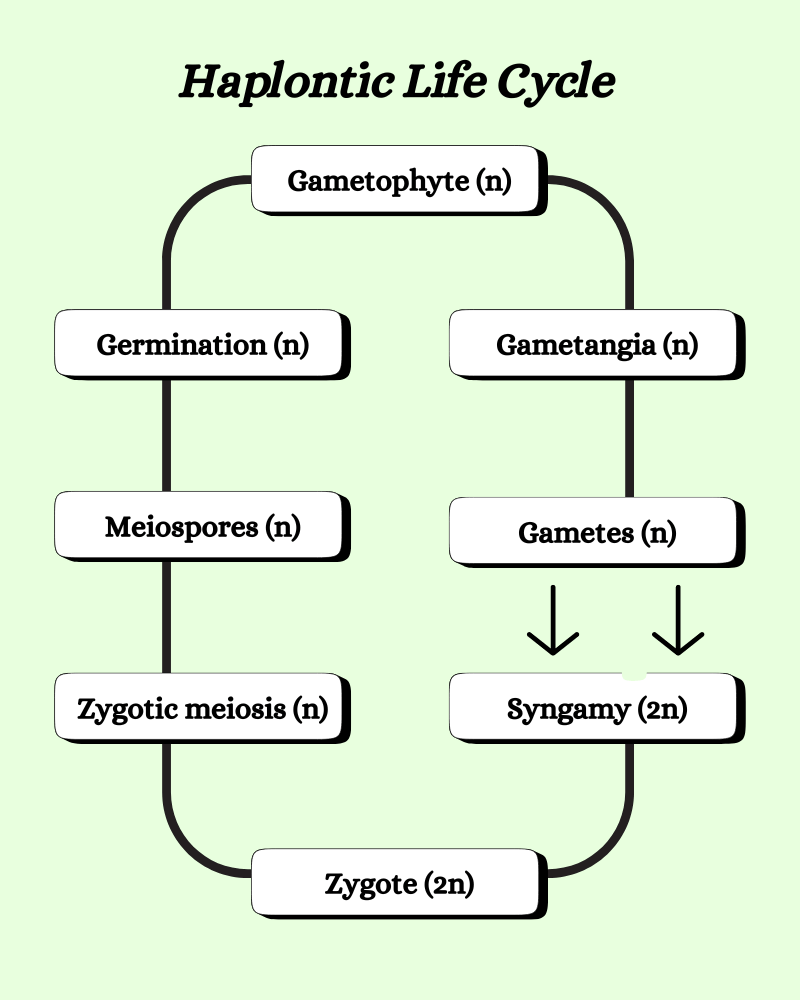
- The plant body produces male and female gametes via mitosis.
- These gametes fuse to form the diploid zygote.
- The diploid zygote undergoes meiotic division sooner and is a shorter phase.
- Zoospores are formed after the zygotic meiosis that will germinate into new plants.
- The new plants mature and produce gametes through mitosis; thus, the life cycle continues.
- Eg. Chara bangia, Chlamydomonas, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, and Ulothrix.
Diplontic types of life cycle in algae
In the diplontic life cycle, the prominent phase. The plant body is sporophytic or diploid. The haploid stage is displayed only by the gametes which will fuse to form the next diploid phase- the zygote.
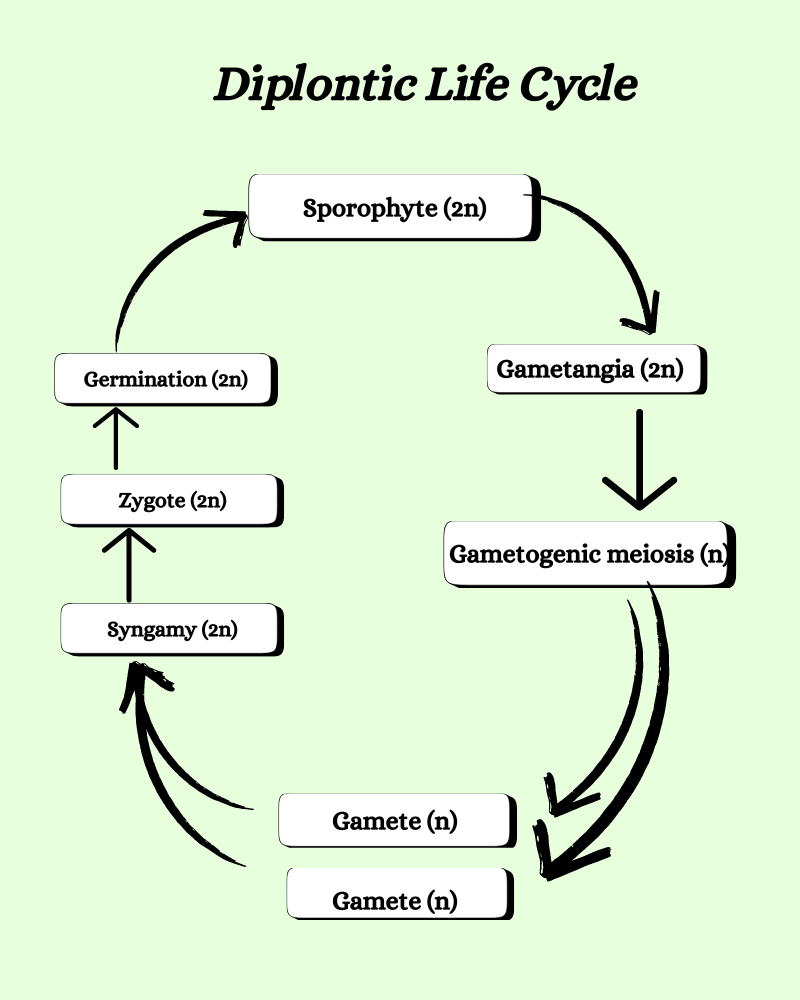
- The diploid plant body produces male and female gametes through meiosis.
- The gametes undergo syngamy to produce a diploid zygote.
- The zygote develops into the sporophytic plant.
- The sporophytic plant will later undergo meiosis to produce the gametes.
- Eg. Codium, Fucus, and Sargassum.
Haplodiplontic or Diplohaplontic types of life cycle in algae
Both terminologies- haplodiplontic or diplohaplontic are correct as this type of life cycle has equal importance to the haploid and diploid phases. These are not short-lived but have a significant duration through the life cycle. The haploid phase has the gametes and meiospores, while the diploid phase has the zygote and the sporophytic body that produces meiospores.
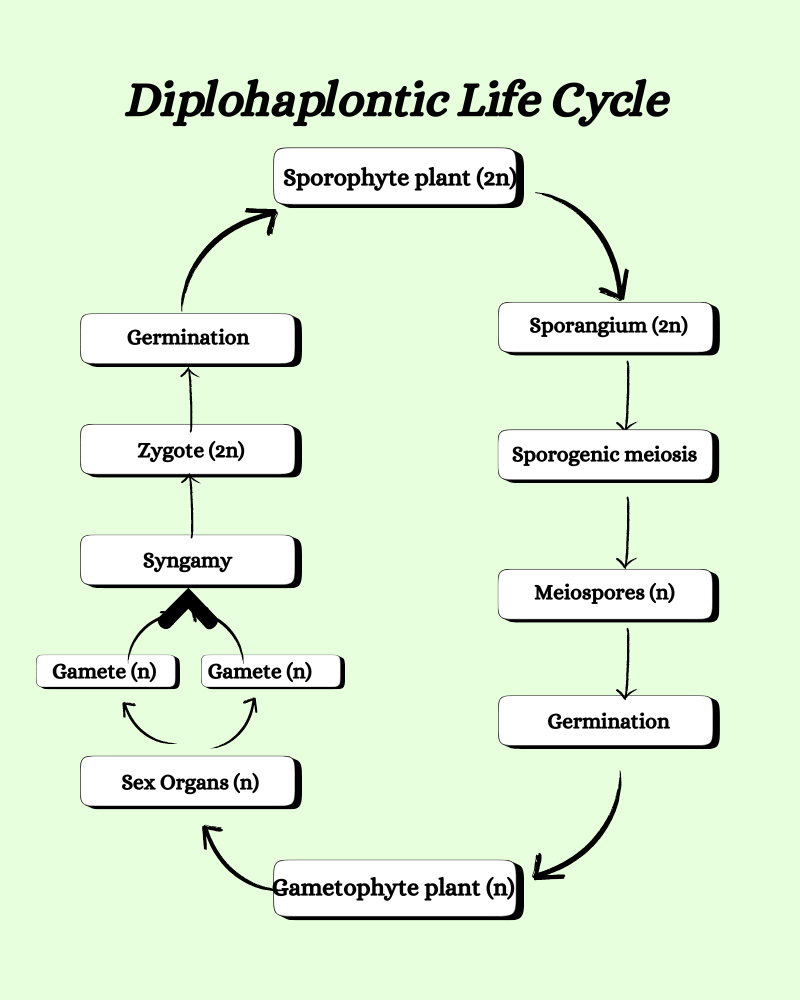
- The plant body is a gametophyte which will produce the respective male and female gametes that will fuse to form the zygote.
- The zygote will germinate to grow into the sporophyte (diploid), producing the spores later.
- The sporophyte undergoes meiosis to produce meiospores.
- These meiospores will germinate to form the gametophytic plant body.
Depending upon the morphological similarity of the gametophyte and sporophyte phases, the haplodiplontic life cycle is of two types.
- The isomorphic or homologous type where the gametophytic and sporophytic plant bodies are similar in morphology but differ genetically. Eg, Cladophora, Dictyota, Ulva.
- Heteromorphic type has gametophytic and sporophytic plant bodies different in morphology and genetics. They are also different in size with the sporophyte being larger than the gametophyte or vice versa. Eg. Cutelaria, Desmaresita, Laminaria, Urospora.
Haplobiontic life cycle- Diphasic
This phase is also known as haplohaplontic. Here, the prominent phase is gametophyte. There are two haploid phases and one diploid phase. The zygote is the only diploid phase. The gametophytic plant body and carposporophyte represent the haploid phases.
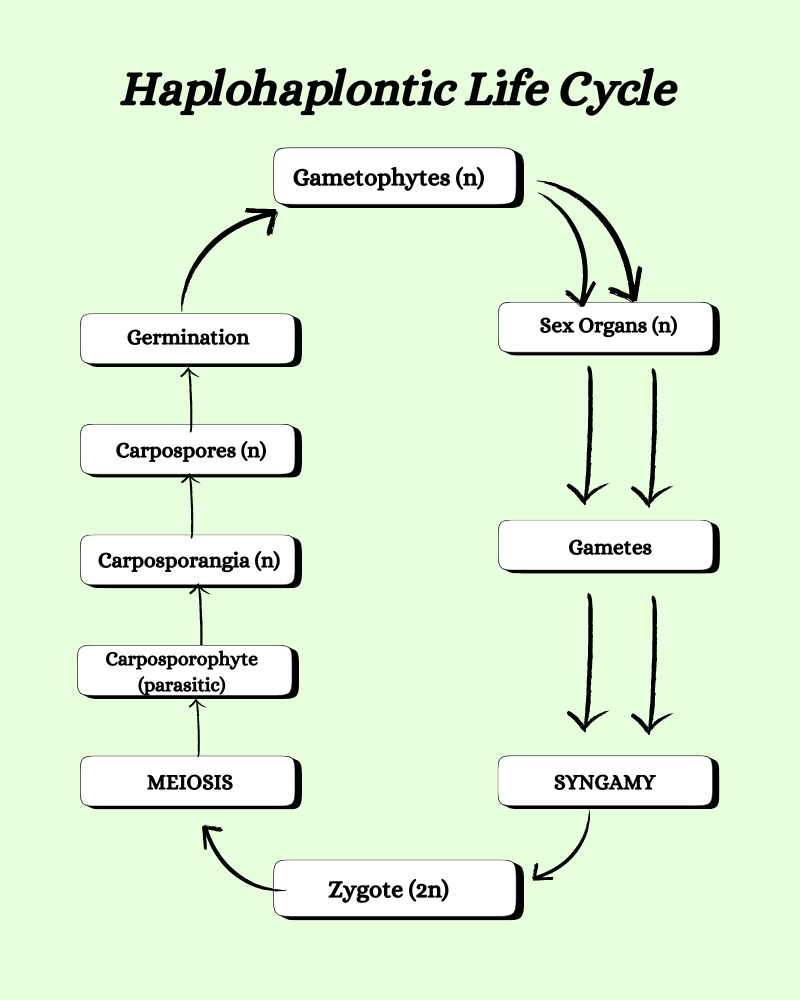
- The plant body produces male and female gametes.
- The gametes fuse to form the zygote.
- The zygote undergoes meiosis to produce carposporophyte.
- The carposporophyte produces carpospores.
- These carpospores germinate to form the gametophytic plant body.
- Eg, Nemalion, red algae
Triphasic Haplobiontic life cycle
This triphasic haplobiontic life cycle includes three phases- two phases of one haploid and a diploid phase each. This is similar to the haplobiontic life cycle with two haploid phases. The only exception or addition here is the presence of the Chatrant Stage that comes after the carpospores. Thus it is also called haplohaplohaplontic life cycle. This is seen in Batrachospermum.
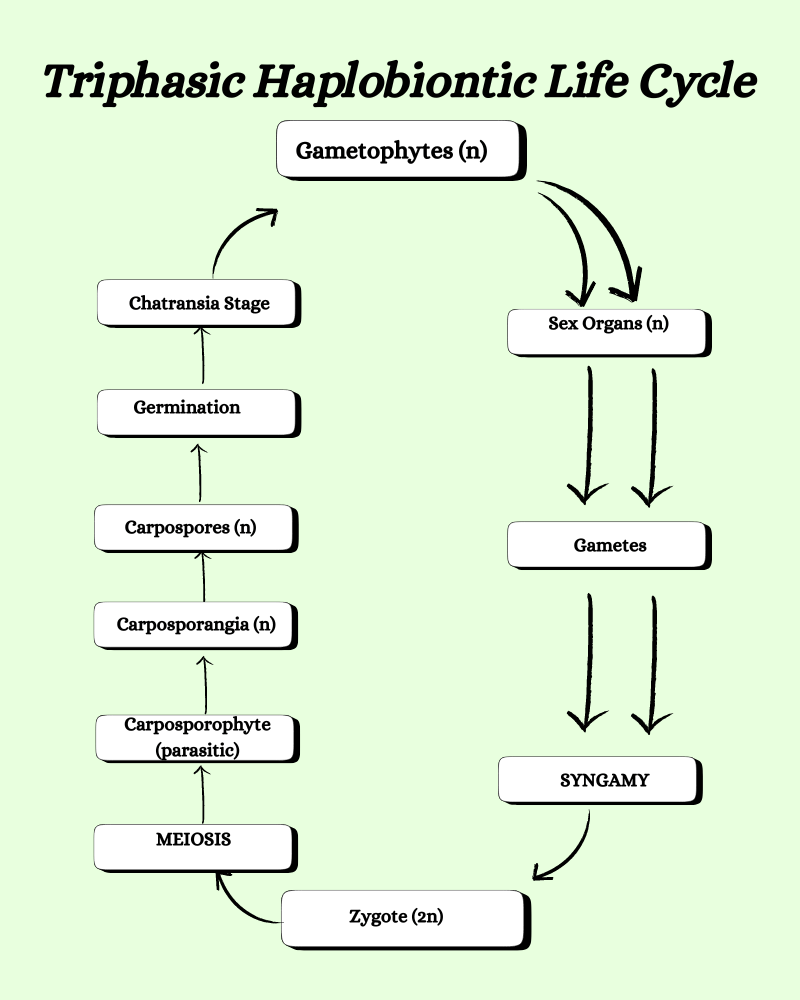
- The haploid plant body produces a glomerulus which will later give rise to the antheridium and carpogonium.
- They in turn produce sperm and eggs that undergo fertilization. The resulting zygote is diploid which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid cystocarp or carposporophyte.
- Carpospores are produced from this which will germinate into a gametophytic structure Chatransia. This is a temporary stage.
- The Chatransia stage will produce special branches from which the gametophytic plant body is developed.
Triphasic Diplobiontic types of life cycle of algae
In this type of life cycle, the prominent phase is diploid but the plant body is haploid. The haploid phase is represented only by the plant and its gametes. The diploid phase is two in number- a carposporophyte and a tetrasporophyte.
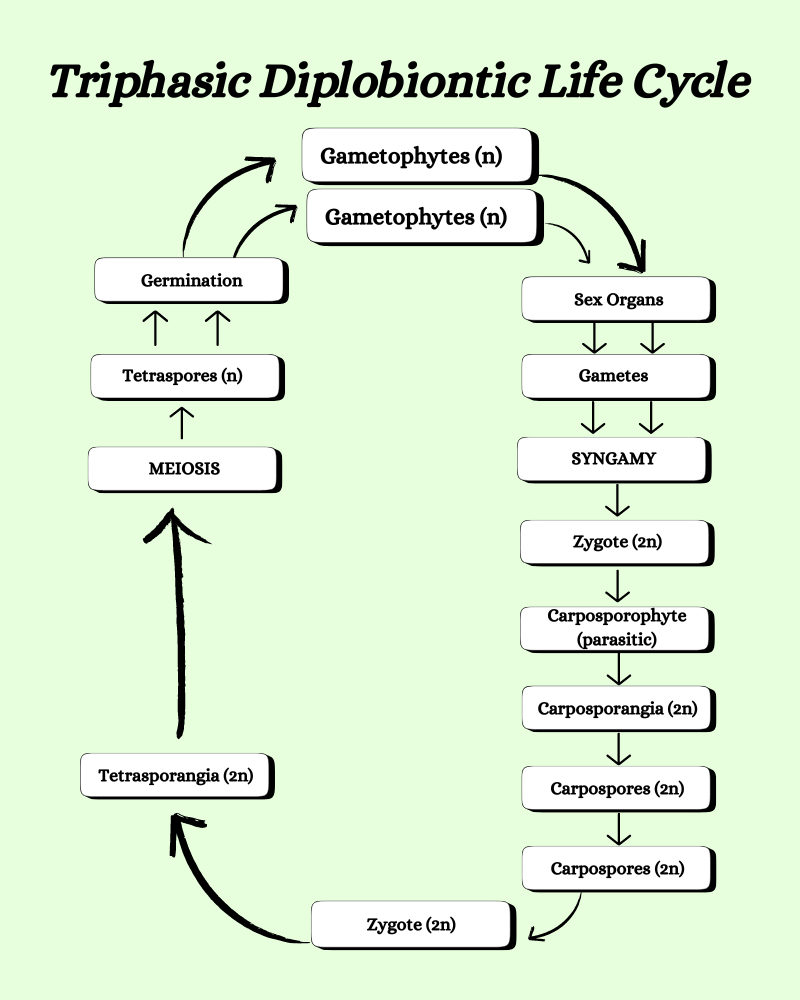
- The gametophytic plant body produces gametes that undergo fertilization and produce the zygote.
- The diploid zygote germinates into a carposporophyte.
- The carposporophyte produces carpospores.
- Carpospores germinate into the next diploid phase tetrasporophyte.
- Tetrasporophyte produces haploid tetraspores by meiotic division.
- These tetraspores germinate into the plant body.
- Polysiphonia has an isomorphic life cycle where the two independent phases have plant bodies similar in genetics and morphology.
- Members of Nemalionales have a heteromorphic life cycle as their plant bodies are dissimilar in two phases.
Additional Reading
- Zygotic Meiosis Life Cycle in Algae
- Sporic Meiosis Life Cycle in Algae
- Somatic and Gametic Meiosis Life Cycle in Algae