One of the main importance of vitamin K helps with blood clotting, it is also called coagulation vitamin or antihemorrhagic factor.
In 1929, a Danish investigator, Henrik Dam discovered that the chickens fed on an artificial diet suffered a haemorrhage due to prolonged periods of blood clotting. Later in 1934, he coined the term Vitamin K (k stands for Coagulation in Danish) for the vital compound that cured this condition.
Characteristics of Vitamin K
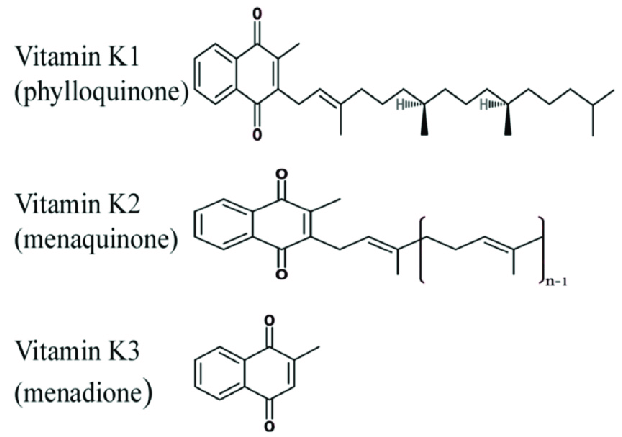
- Vit K exists in two forms- Vit K1 and Vit K2 found in plants and animals, respectively.
- Vit K1 is found in alfalfa, cabbage, spinach, etc.
- Vit K2 is found in putrefied fish meal and intestinal bacteria.
- Both types of Vit K are derivatives of quinones.
- They differ in the side chain of Carbon 3 of naphthoquinone ring- Phytol radical in Vit K1 and farnesyl pyrophosphate in Vit K2.
- Vit K1 also has 4 units of isoprene in its side chain whereas Vit K2 has 6 units of isoprene with a double bond in the side chain.
Properties of Vitamin K
- Vitamin K1 appears as a yellow viscous oil while Vit K2 has the same color but is crystalline in form.
- Both are sensitive to light and must be stored in the dark to avoid spoilage.
- Vulnerable to irradiation, alkalies, acids and oxidizing agents.
Metabolism of Vitamin K
- Vitamin K is essential for the formation of prothrombin, the blood plasma protein required for blood clotting.
- When humans consume Vit K1 found in plants, the intestinal bacteria convert it into Vit K2 for storage.
- The body loses its power to clot the blood in the absence of this vitamin.
- Infants may develop haemorrhage due to its deficiency. It could be prevented by taking this vitamin during pregnancy.
- A deficiency of vitamin K could also cause lower fat absorption in the body and excess fat or lipid excretion.
Importance of Vitamin K
- Prevent fractures due to osteoporosis and osteopenia.
- Could prevent liver cancer and reduce fatality due to liver cirrhosis.
- Reduce vascular calcifications.
- Reduce the risk of coronary heart disease.
- May improve insulin sensitivity and increase glucose tolerance.
References
- What to know about vitamin K-2
- Vitamin K
- Asmar, Margueritta & Naoum, Joseph & Arbid, Elias. (2014). Vitamin K Dependent Proteins and the Role of Vitamin K2 in the Modulation of Vascular Calcification: A Review. Oman Medical Journal. 29. 172-177. 10.5001/omj.2014.44.
- DiNicolantonio, J. J., & Bhutani, J. (2015). The health benefits of vitamin K. Open Heart, 2(1), e000300. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2015-000300
Additional Reading
- Properties And Biological Role Of Vitamin A
- Properties and Biological Importance of Vitamin B
- Biological Role and Properties of Vitamin C
- Properties And Biological Role of Vitamin D
- Properties And Biological Importance Of Vitamin E