Elmer McCollum demonstrated the first existence of vitamin D in 1922. Due to its effects in treating rickets disease caused by rats, vitamin D is also called an antirachitic factor. As the human body synthesizes this vitamin when exposed to sunlight, it is called the sunshine vitamin as well.
Characteristics of Vit D
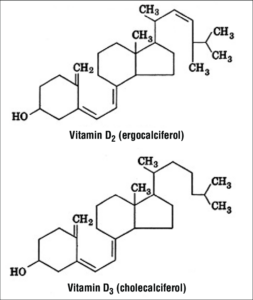
- Vitamin D exists in various forms, of which Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3 are the important ones.
- They are called ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol respectively.
- Cod liver oil is the best natural source of vitamin D.
- Egg yolk, dairy products, and some fruits and vegetables also contain this vitamin but in smaller amounts.
- Vit D2 has a plant origin while Vit D3 originated from animals.
Structure and Properties of Vit D
- Vitamin D2 is produced from ergosterol in plants by its irradiation by ultraviolet light.
- Vit D3 is produced from 7-dehydrocholesterol in animals through a similar process.
- The molecule has a steroidal structure with four rings.
- The main structural difference between the D3 and D2 versions is the presence of a double bond in the D2 molecule, existing between the carbon atoms 22-23. It also has a methyl group in C24.
- Vit D is an odourless, white crystalline, fat-soluble substance.
- It is heat resistant and oxidation resistant and is also not affected by alkalis or acids.
Metabolism of Vitamin D
Under the UVB light, 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermis of humans undergo a chemical reaction to initially form pre-vitamin D3. This is a non-enzymatic reaction. This will further make internal changes in the molecule to give rise to Vit D3.
- Vitamin D3 thus formed is transported to other parts of the body with the help of VDBP binding.
- Only one-half of the produced vitamin is transported to the liver where further processing happens until it is transformed into its circulating form.
- The other half is stored in the adi[ose tissues. This will be stored for up to 2 months.
- In the liver, Vit D is converted into its useful form of 25OHD3, with the help of a cytochrome.
- The conversion of the circulating form of Vit D into its active form takes place in the kidneys.
- In the kidney tubules, the 25OHD3 molecules undergo 1-alpha hydroxylation to form 1,25 (OH) 2D3 with an additional OH group in the first carbon of A ring.
- The 23-hydroxylase enzymes in the inner membrane of mitochondria in kidney cells perform a stepwise reaction to convert the active form of Vit D3 into an inactive calcitroic acid.
Biological Importance of Vit D
- The primary role of vitamin D is to help the body absorb, retain, and utilize calcium and phosphorus. Both of these are necessary to build bone structure.
- Studies have also shown that it can help reduce inflammation, prevent cancer cell growth, and control infections.
- Deficiency of this vitamin leads to health issues in the bones, inflammations, lower immunity, and rickets disease.
Additional Reading
- Classification of Vitamins With Examples
- Properties And Biological Role Of Vitamin A
- Properties and Biological Importance of Vitamin B
- Properties And Biological Importance Of Vitamin C