Write a Short Note on Properties of Vitamin C
It was Albert Szent-Györgyi in the 1930s who discovered ascorbic acid. This discovery was a significant milestone as well as a foundation for modern nutrition studies. In the 1970s, Linus Pauling promoted the extensive use of vitamin C to prevent and treat common colds.
Characteristics of Vitamin C
- Ascorbic acid otherwise known as Vit C is one of the most important vitamins required by the human body.
- It is also one of the most powerful natural antioxidants which helps boost natural immunity. While most mammals can produce vitamin C in their body, humans cannot synthesize it.
- The major source of vitamin C is the diet.
- Vit C is water-soluble and delivered to every cell in the body. But the cells do not store this vitamin and thus it is needed on a per-day basis.
- This vitamin is present in various fruits and vegetables but is most abundant in Amla or Indian Gooseberry, followed by citrus fruits like lemon and oranges.
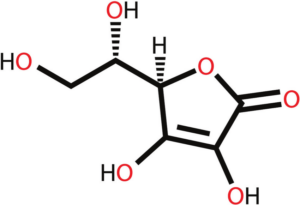
Structure of Vitamin C
- The chemical name of Vit C is l- ascorbic acid or ascorbate.
- It is otherwise known as an antiscorbutic vitamin
- With an asymmetrical six-carbon structure with a molecular formula of C6H8O6.
- Its structure is similar to that of a glucose molecule.
Properties of Vitamin C
- This water-soluble vitamin forms a colorless or slightly yellow-coloured liquid when dissolved.
- Vitamin C functions as a reducing agent that neutralizes the oxidants in the cells.
- It is a weak unstable organic molecule that can easily undergo oxidation and is destroyed.
- It is vulnerable to high temperature, oxygen, humidity, light, heavy metals, and metals such as copper, alkaline medium, etc.
- Vitamin C exists as derivatives of sodium, calcium, zinc, palmitic acid, etc.
Metabolism of Vitamin C
The main function of Vit C is reducing the harmful oxidants which may or may not be a reversible reaction. These reactions are solely dependent on the pH changes. Only the l-ascorbic acid is the active Vit C. Ascorbic acid can undergo a three-step oxidation process to become a more potential reducing agent. Some of these processes are reversible and some are irreversible.
- Under high heat, alkaline medium, and in the presence of copper, ascorbic acid undergoes a reversible oxidation reaction to form dehydroascorbic acid. This product has a shorter life of a few minutes before it is further oxidized through a reversible or irreversible process.
- In an acidic pH of 4, the oxidation of dehydroascorbic acid is irreversible and produces 2,3-diketo-l-gulonic acid or diketogulonic acid. This process that starts in milder acidic conditions can progress rapidly with the presence of an alkaline medium to produce diketogulonic acid which is a more powerful reducing agent.
On the other hand, in the same acidic conditions in the presence of hydrogen sulfide, the same dehydroascorbic acid is oxidized back to ascorbic acid. This is a reversible process.
Both ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid show antiscorbutic (effect on scurvy) properties.
- In alkaline conditions of pH 7 to 9, the oxidation of diketogulonic acid results in l-threonic acid and oxalic acid.
The reversible oxidation reactions of ascorbic acid happen in alkaline medium in the presence of H2S and glutathione. The oxidation of high doses of vitamin C results in the production of CO2 as a product.
Ascorbic acid is the reduced form of Vit C and dehydroascorbic acid is its oxidized form. Vit C is seen in its reduced form of ascorbic acid in human cells.
Biological Importance of Vitamin C
Vitamin C has a wide range of biological roles inside the body.
- Boosting immunity and reducing inflammation
- Vit C helps maintain healthy immunity by regulating and enhancing adaptive and innate immunity.
- Its antimicrobial properties can neutralize the toxins produced by infectious bacteria.
- Promotes phagocytic properties of immune cells.
- Increases antibody production and proliferation of lymphocytes.
- High doses of Vit C reduce inflammation in the joints and other cells in the digestive system, respiratory system, etc.
- The antioxidant property of vitamin C is because of its non-enzymatic reducing power. It freely donates electrons to the free radicals and reduces them to harmless components.
- Depigmentation: Vit C is an excellent remedy for skin pigmentation. It can immensely reduce melanin production by reducing the free radicals that trigger melanogenesis.
- Collagen production: Vit C is an important factor in the production of collagen. It enables the hydroxylation of proline, activates procollagen mRNA, inhibits MMPs that degrade collagen fibres, and activates fibroblast for the production of new collagen.
- Vit C increases the intestinal absorption of iron by enhancing the reduction of iron. Reduced iron is better absorbed by the intestinal cells.
- Taking high doses of vitamin C helps factory workers who are exposed to heavy metals to have better health and reduced levels of these metals.
- Nutrient absorption: Several nutrients such as Vit E, folic acid, Vit B15, tryptophan, etc require the presence of Vit C to be absorbed by the cells.
- Absorption of contraceptive pills and estrogen is increased when there is an adequate amount of vitamin C.
- Lipid metabolism: Vit C protects lipids from oxidation and reduces LDL levels. It can function as a cofactor for various biosynthesis to reduce the high levels of bile salts and cholesterol.
- Bone formation: An adequate amount of vitamin C helps maintain bone density and can prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
- Reduce stress by controlling the production of cortisone.
A deficiency of ascorbic acids leads to Scurvy that shows loss of collagen, and haemorrhages causing teeth loss and affecting bones in children.
Additional Reading
- Classification of Vitamins With Examples
- Properties And Biological Role Of Vitamin A
- Properties and Biological Importance of Vitamin B