The nucleolus is the prominent and spherical area in a nucleus which is made of acidophilic colloidal bodies. Here is the details of the basic structure and function of nucleolus.
Characteristics of Nucleolus
The number of nucleoli depends on the synthetic activity of the cell. More active cells will have a larger nucleolus.
- The nucleolus is eccentric in position.
- It is associated with nucleolar organizing chromosomes.
- The nucleolar organization is often a darkly stained knob-like structure having genes of 28s, 18s, and 5.85s rRNAs.
- The nucleolus is non-membraneous.
- Its organization remains intact by Ca+ ions.
- Apart from the DNA and rRNAs that are part of the nucleolar organization, the nucleolus contains 70 types of ribosomal proteins, nucleolin, and RNA-splicing nucleoproteins.
- Other components include Ca2+ ions, phospholipids, orthophosphates, phosphatase, nucleoside phosphorylase, nucleotides, rRNA, etc.
- Some cells have RNA methylase as well.
The nucleolus disappears during mitosis and meiosis in the prophase. It first reduces its size and as the chromosome condenses and RNA synthesis stops, the nucleolus disappears. There is no nucleolus in the metaphase.
It reappears at the end of telophase as a tiny nucleolus at the ribosomal RNA genes. The RNA and protein components that are disintegrated are carried to each daughter cell. When the nucleolus reappears in telophase, it helps the nucleus to reestablish itself.
Structure of Nucleolus
The nucleolus has three regions that are part of the initiation, production, and maturation of RNAs.
Fibrillar Centre
The fibrillar center is the lightly stained innermost region. The genes of RNas of nucleolar organizing chromosomes are in this region. Transcription of rRNA synthesis occurs in this region.
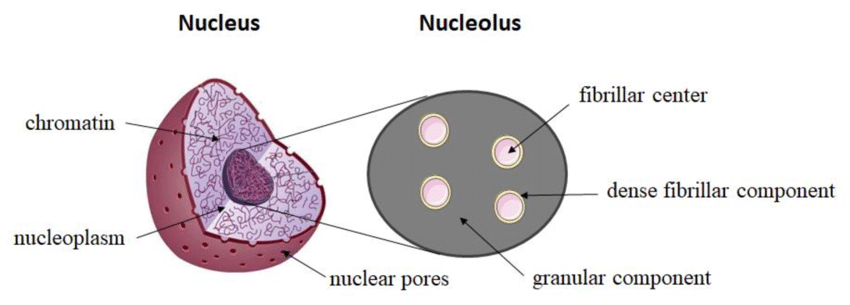
Dense Fibrillar Component
This dense fibrillar component progresses with the binding of 70s ribosomal proteins to the transcripts.
Cortical Granular Components
Corticalgranular components are the outermost region where the pre-ribosomal particles are matured and processed.
Functions of Nucleolus
- The nucleolus is the site of biogenesis of ribosomal subunits such as 40s and 60s.
- As part of a longer precursor molecule of 45s transcript, 28s, 18s, and 5.8s types of rRNAs are transcribed here.
- Processing of these RNAs is done with the help of nucleolin and U3snRNP (small nuclear Ribosomal Nuclear Protein),
- The 5s rRNA transcribed outside the nucleolus and the 70sribosomal proteins synthesized in the cytosol are assembled in the nucleolus.
- They are assembled into subunits and are transported back to the cytosol.
- The 40s subunits are transported earlier than the 60s subunits to prevent their access to the incomplete heterogenous RNA that is under processing.
References
- Agarwal, P. V. |. V. (2004). Cell biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution, and Ecology: Evolution and Ecology. S. Chand Publishing.
- Humeau, Juliette. (2019). Inhibition of Transcription by Dactinomycin Reveals a New Characteristic of Immunogenic Cell Stress.
Additional Reading
- Endoplasmic Reticulum in Plant Cell
- Biochemistry and Structure of the Nuclear Envelope
- Structure and Function of the Nucleus